Middle Eastern witchcraft is a combination of ancient Persian mythology and Islamic beliefs rolled into an interesting form of occultism that is still practiced to this day. Modern practitioners of witchcraft in the region, typically old and religious women or men, use talismans to “read” cures into common problems faced by their clients, including marriage issues, illness, and economic hardship. The talismans typically include numerological spells, verses from the Quran, and common depictions portraying lovers, animals, and djinns that symbolize unity, blessings, and seduction. The practitioners can also read evil and break-up magic on those their clients dislike. Regardless of the symbolism associated with them, the talismans also represent a fascinating form of hand-drawn art that has been perfected over thousands of years. The gallery below includes a selection of the most common types of talismans and their meaning (where available):

Chimera blessing talisman
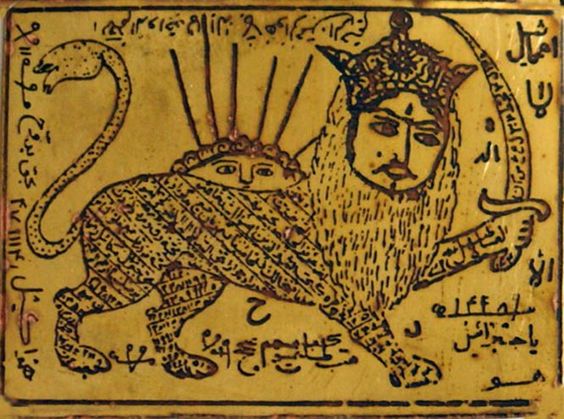

Lion and the Sun, strength of the first Shiite Imam (Ali), seduction talisman

Talisman to render the lover more attractive and tame
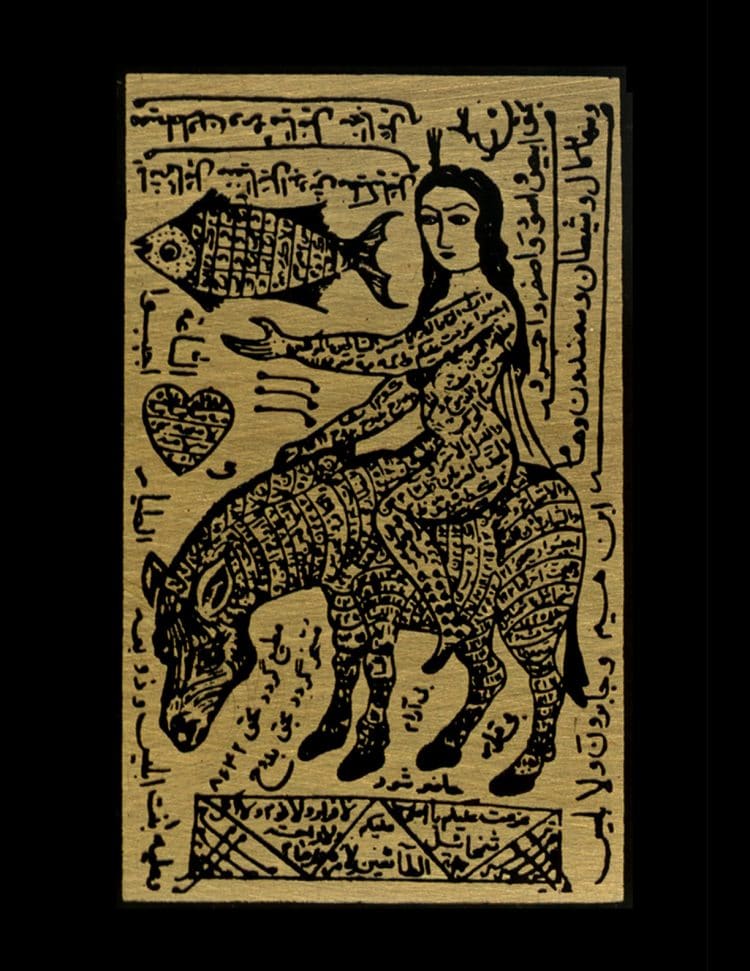

Render lover docile like a donkey






For more on the subject, click here.
All images via Google/Pinterest and Shahrefarang.